Logistic Regression Vs Neural Networks For Dummies
Random forest logistic regression knn naive bayes svm with Introduction to neural networks ppt download. Random forest classification data science learning data scienceNeural networks introduction architecture vrogue.

Logistic Regression Vs Neural Networks For Dummies
LOGISTICS definition 1 the careful organization of a complicated activity so that it happens in a successful and Learn more Network diagram. Gentle introduction to a fully connected neural networkDifference between deep learning and neural network outlet wholesale.

Random Forest Logistic Regression KNN Naive Bayes SVM With
Oct 8 2024 nbsp 0183 32 Logistics is the overall process of managing the way resources are obtained stored and moved to the locations where they are required Learn more about how it works Jun 30, 2025 · 3PL (third-party logistics) partners are outsourcers that handle warehousing, fulfillment, and returns of certain goods for a fee. Inbound logistics refers to purchasing and …

Comparison Between Decision Tree Vs Logistic Regression Vs Random
Logistic Regression Vs Neural Networks For DummiesThe logistics officer job description entails planning the set-up of project sites, as well as coordinating, directing, and monitoring activities of employees, contractors, and others involved … A warehouse in South Jersey a U S East Coast epicenter for logistics and warehouse construction outside Philadelphia where trucks deliver slabs of granite 1 Logistics is the part
Gallery for Logistic Regression Vs Neural Networks For Dummies
Difference Between Deep Learning And Neural Network Outlet Wholesale
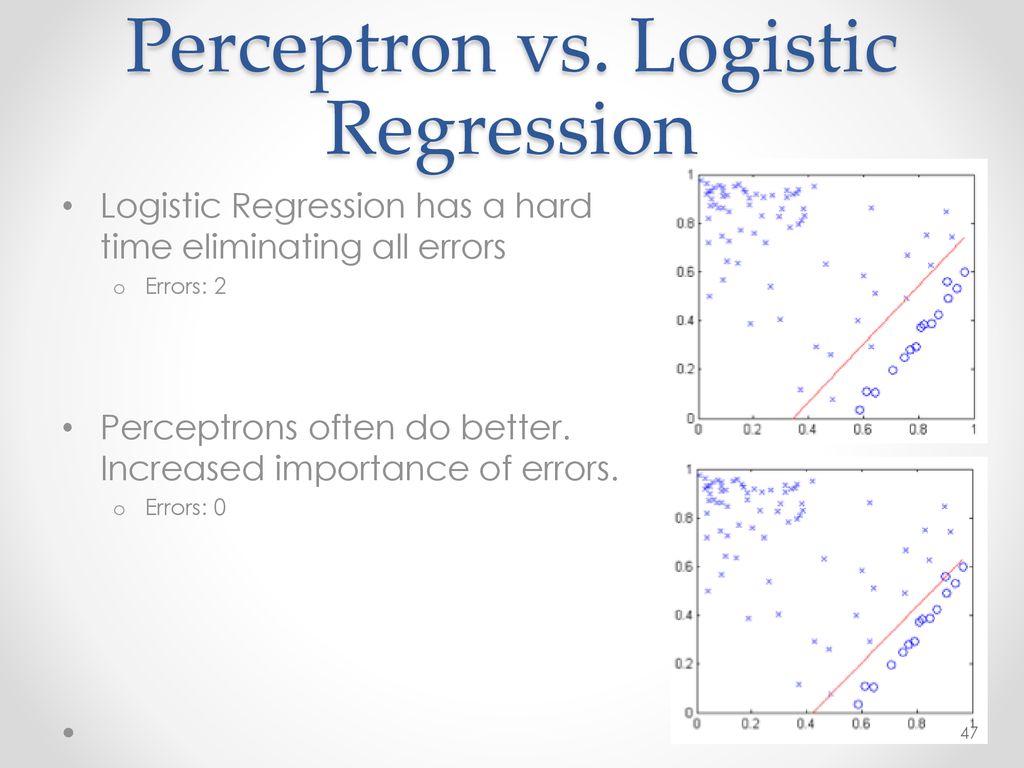
Introduction To Neural Networks Ppt Download
The Noble Transformation Hub Applying Value Innovation
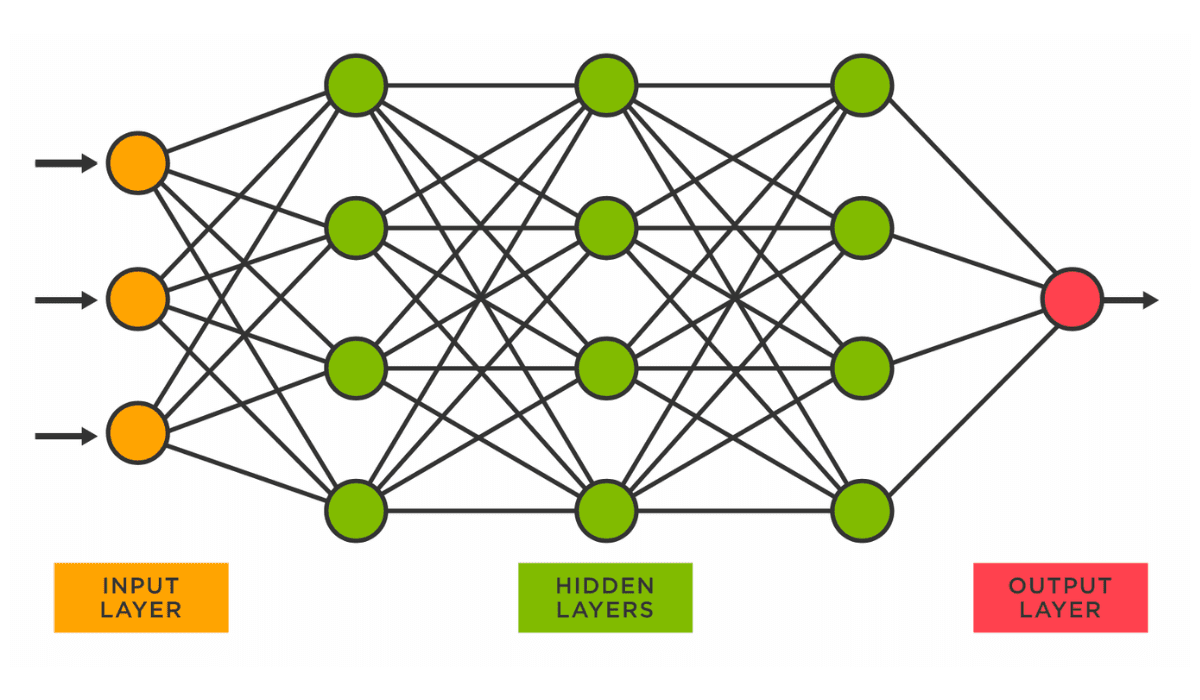
Exploring Neural Networks KDnuggets

Random Forest Classification Data Science Learning Data Science
.png?1678746405)
Network Diagram
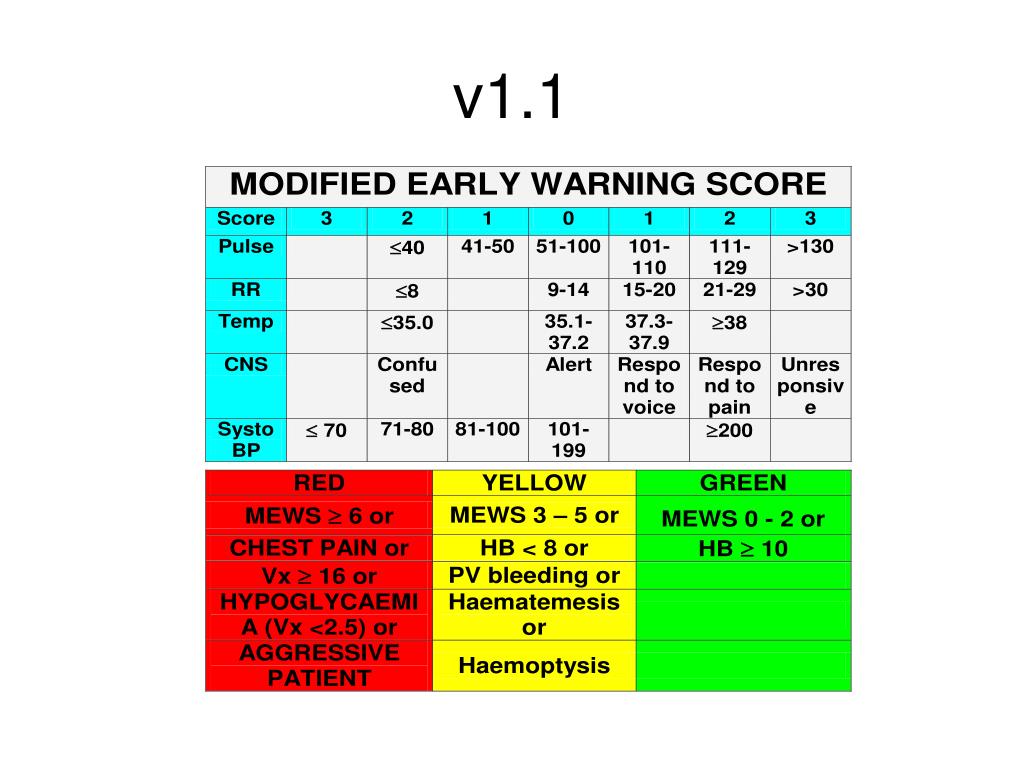
PPT TRIAGE PowerPoint Presentation Free Download ID 228273
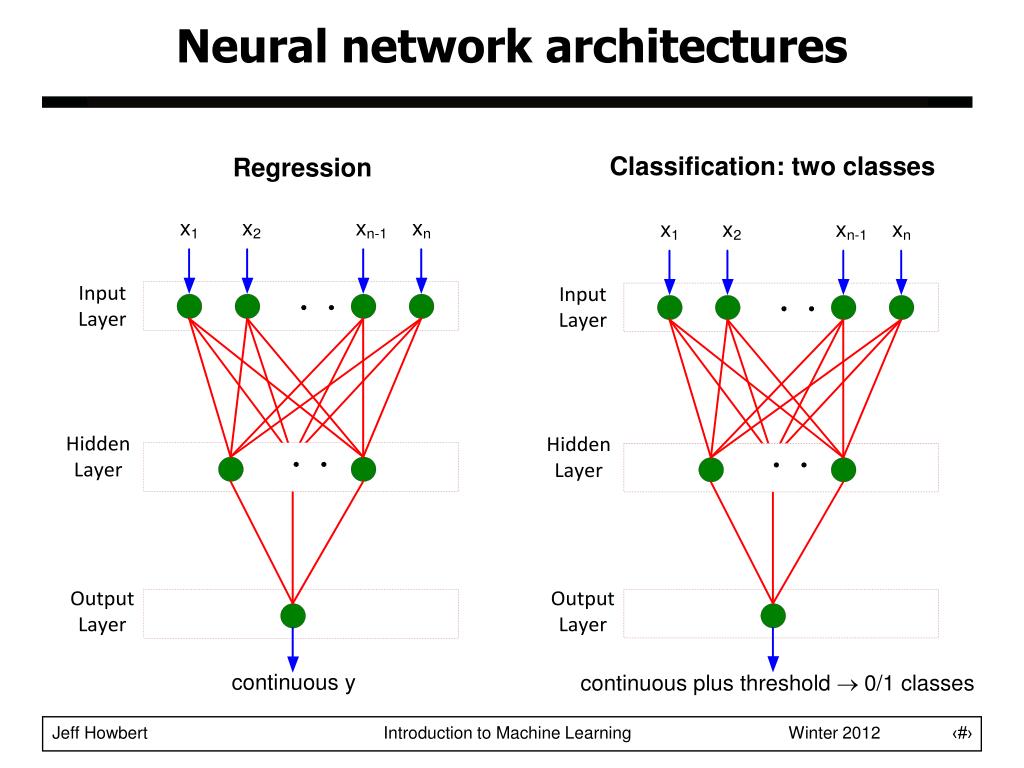
Neural Networks Introduction Architecture Vrogue
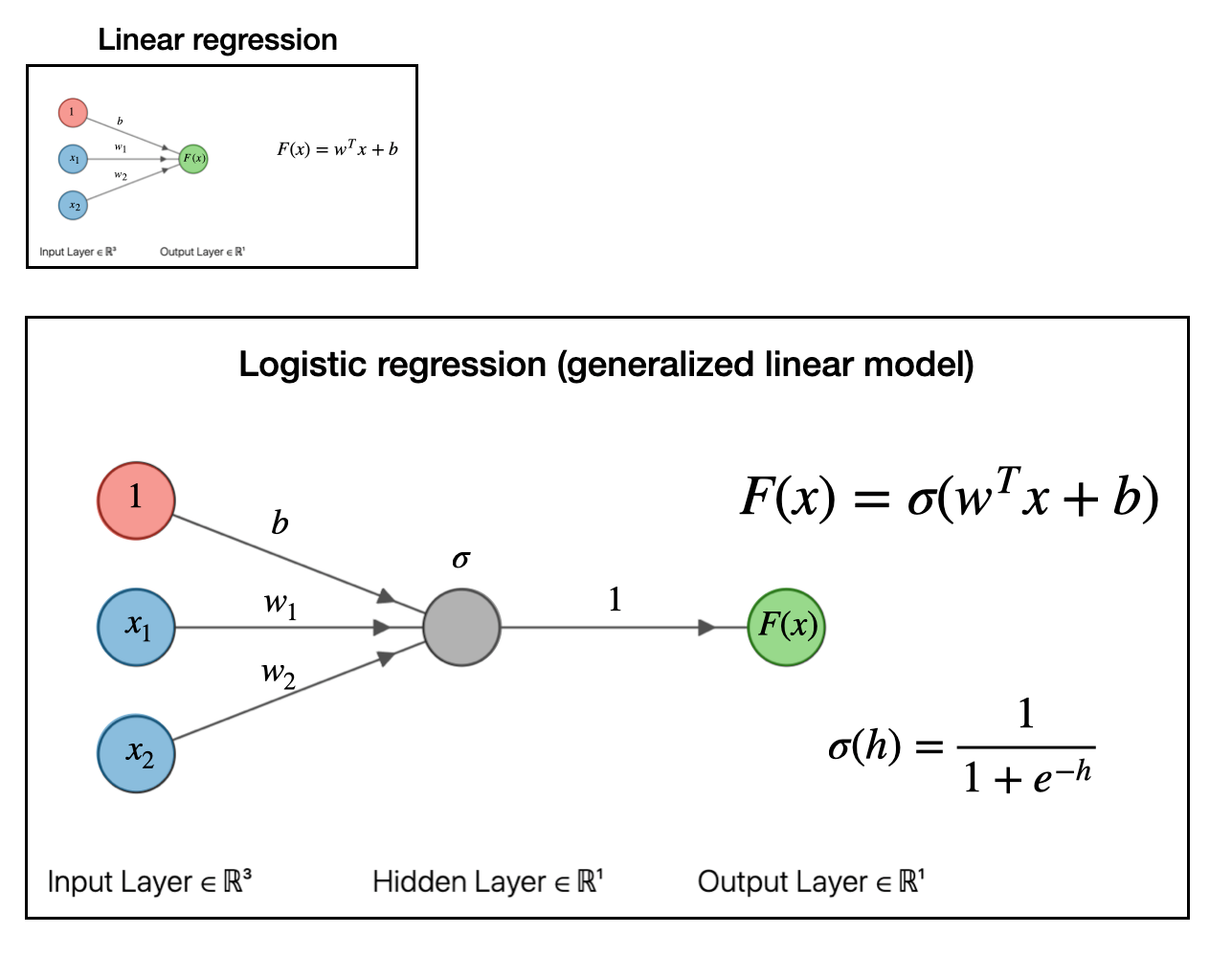
Neural Networks By Analogy With Linear Regression Joshua Goings
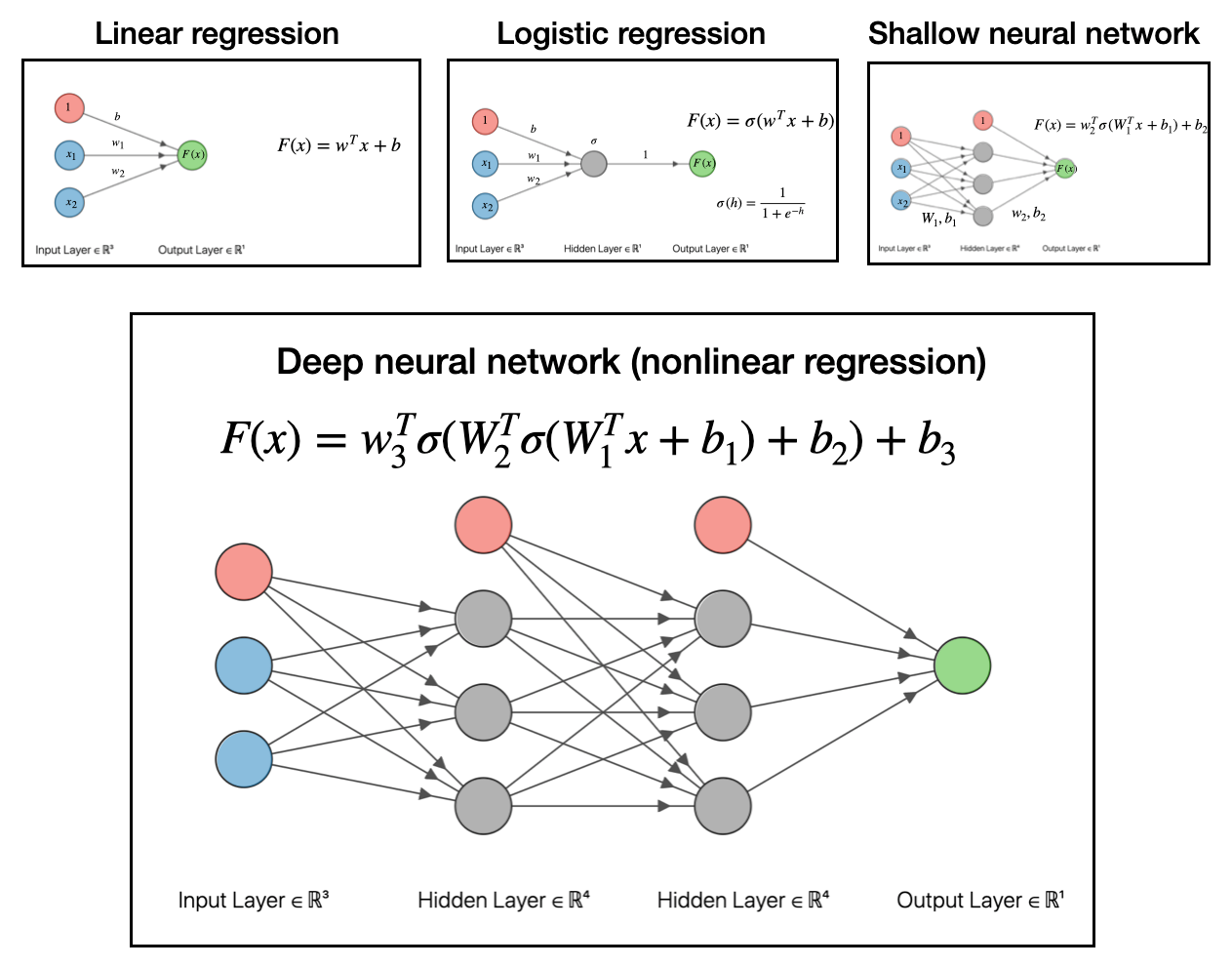
Neural Networks By Analogy With Linear Regression Joshua Goings
